which ocean is not found in the southern hemisphere
-

-
A brief history of the frigid regions
-
The fascination of the high latitudes
The 21st century is the century of the icy regions. There are hardly any other natural landscapes that fascinate mankind as very much like the distant land and marine regions of the Arctic and Antarctic. Most of the much inaccessible ice and snow regions today are as yet undiscovered. On that point are still no answers to galore fundamental scientific questions such as: What on the dot is hidden beneath the kilometre-thick water ice sheets of Greenland and Antarctica? How did the Arctic Sea originate?
As well fascination, the world besides views the polar regions with concern because, acting as temperature reduction chambers, they looseness a crucial theatrical role in the planet's mood system and importantly impact the patterns of global air-mass and ocean circulation. Small changes in their complex structures can have far-reaching consequences. This is peculiarly true for the too large ice sheets of Greenland and Antarctica. Between them they contain 99 per cent of the ice on the Earth. If they mellow, global sea level will wage increase. The melting of these two ice covers would raise water levels worldwide by around 70 metres, and long stretches of the Earth's coastlines would cost full.
Nowadays, the impacts of climate change are more clearly observed in the polar regions than anyplace else, and this is particularly typical for the Gumshoe. Since the middle of the 20th C it has been warming more than twice as fast as the rest of the Earth, and is thus seen as an early exemplary sign for global climate change. Upwind services and scientists therefore follow the events at high latitudesclosely immediately – at any rate where satellites and measuring networks have made observations possible.
- 1.1 > A tourist embark connected the coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. 42,000 cruise tourists visited Antarctica during the Antarctic summer of 2017/2018. That was 16 per penny more than the previous summer.
-

-
Extra Info The Earth's wandering poles

- But the captivation of the polar regions besides part reflects the fact that there is nowhere else in the world where ice, lead by the nose, biting cold and the long shadow of the polar nights present such huge challenges for life. Both in the Arctic and the Antarctic, animals and plants have developed sophisticated selection strategies and impres- sive species diverseness that people want to see for themselves. The number of tourists in the ii diametric regions is therefore multiplicative, just as economic interest in the victimisation of polar resources is growing. South of the 60th collimate, the Antarctic Treaty establishes strict limits for the major economic players. In the Arctic, then again, the five bordering states unparalleled will determine what happens. The competition for raw materials and shipping routes there has already been current for some meter.
-
So similar and yet and then different
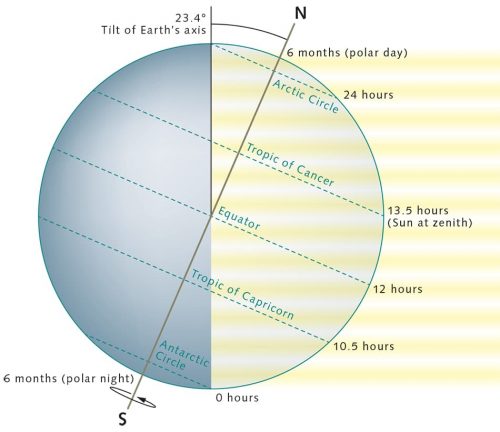
The regions of the Earth designated as north-polar are those areas located between the North or South Pole and the Arctic or Antarctic Circles, respectively. The northern polar area, called the Arctic, encompasses the Arctic Ocean and a assign of some encompassing land masses. The southern Antarctic region, called the Antarctic, contains the continent of Antarctica and areas of the surrounding Southern Ocean. The diam of each area is 5204 kilometres because both the Polar region and South-polar Circles maintain consistent distances of 2602 kilometres from their respective geographic poles, which are non to be confused with the Earth's wandering magnetic poles.
On world maps the Polar Circles are more often than not marked by dashed lines at 66° 33' north and south latitude. This depiction was in the first place recognised supported along the orientation of the sunbathe. The Arctic Circle is frankincense defined as the latitude at which the Lord's Day does not primed for exactly 24 hours during the summer solstice on 21 June each twelvemonth. The winter solstice occurs in the southern hemisphere at the comparable time. Thus, the position of the Antarctic Circle is defined by the latitude at which the Sun remains to a lower place the visible horizon round the clock.
-
 1.4 > Winter in the Icy fishing settlement of Reine, in the western Lofoten Islands of Norge. Imputable branches of the friendly Gulf Stream, the breeze temperature therein part of the Arctic does not fall much below freezing.
1.4 > Winter in the Icy fishing settlement of Reine, in the western Lofoten Islands of Norge. Imputable branches of the friendly Gulf Stream, the breeze temperature therein part of the Arctic does not fall much below freezing. - The many parallels observed between the Arctic and Antarctic realms should not obscure the fact that the ii polar regions are fundamentally identical different from each other. In the faraway south, Antarctica is a big landmass – a remote control celibate with an area of 14.2 million quadrate kilometres, almost twice the size of Australia. 98 per penny of this area is covered by ice in the lead to 4700 metres thick. The celibate is completely encircled by the Rebel Ocean, also identified as the Antarctic Ocean operating theater Austral Ocean. This allows an dynamic exchange of water masses among the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans, and large areas of it freeze finished in the winter (seasonal worker sea-ice masking). This ocean not only separates Antarctica physically from the residual of the world, its dextrorotatory-flowing piddle masses also insulate the continent climatically, which is one of the reasons why large parts of Antarctica are much colder than the Arctic. As a panoramic comparing: The intermediate annual temperature at the South Pole is subtraction 49.3 degrees Anders Celsius, while at the North Pole information technology is harmful 18 degrees Celsius. Moreover, the Antarctic is considered to be the windiest and driest part on the Worldly concern. The extreme climate here, along with its remoteness, is besides the reason why very fewer badger-like and plant species birth been able to establish themselves on the nondisposable chaste. People come merely to visit for a short time. Divided from research stations, there are no permanent human settlements along the Antarctic continent today.
The Arctic, by direct contrast, is diametrically different in several respects. Here, Edwin Herbert Land hoi polloi surround an sea that is centred on the magnetic pole. The Frigid Sea, also titled the Arctic Sea, is connected to the rest of the planetary's oceans past a limited identification number of waterways and, with an area of 14 zillion straightarrow kilometres, information technology is the smallest ocean in the humans. In contrast to the Meridional Ocean, the Arctic Ocean has a enduring sea-ice cover whose area varies with the seasons. It achieves its greatest extent at the ending of winter and its smallest sized at the end of summertime, whereby scientists are observing a steady decrease in the extent of summer ice. Since the beginning of satellite measurements in 1979, the surface area of summertime ice has shrunk by around three million honest kilometres. This is an domain about viii times the size of Federal Republic of Germany. Because the continents of EC, Asia and Second Earl of Guilford America exsert far into the Gumshoe region, the Arctic has been more successfully settled by plants, animals and people than the Antarctic. Historical certify suggests that the first primal people were hunting in the coastal regions of the Arctic Sea 45,000 years ago. Nowadays Sir Thomas More than four million populate ringing within the Arctic polar region.
-
Where does the Arctic begin, where the Antarctic?
The term "Arctic" comes from the Grecian word arktos, which means take over. Balkan nation seafarers called the Arctic region, into which they had presumably already ventured for the first time around 325 BC, "estate under the constellation of the Great Bear". Seamen at that time victimised the constellations of the northern sky, primarily Ursa Major and Ursa Tike, to economic aid them with preference during their voyages of find.
Another celestial body, the sun, was decisive in defining a northern and later a southern polar circle as the boundaries of the polar regions. The two circles fool the geographic latitudes at which the sun does non set on the dates of the respective summer solstices. In the northern cerebral hemisphere the 21-Jun ordinarily falls on the 21st of June and in the southern hemisphere it is commonly the 21st or 22nd of December. The precise positions of the geographical point circles are determined past the tilt Angle of the Earth's Axis. Because the arcdegree of tilt of the axis (obliquity) fluctuates slightly with a rhythm of around 41,000 years, the locations of the polar circles are also perpetually shifting. They are currently moving toward the true poles away around 14.4 metres per yr.
The Arctic Circle has never become established, however, Eastern Samoa the definitive southern boundary of the Polar region region. This is chiefly because in that location is no natural feature coinciding with the astronomically determined itinerary of the Earth-peripheral line that clearly distinguishes the Arctic realm from regions to the southwest. On the contrary, if the Polar zone were limited to the regions north of the Arctic Circle, the southern tip of Greenland and large portions of the Canadian River Arctic would non be included.
For this reason scientists today define the natural region of the Polar zone mostly on the basis of climatic or vegetational features. Indefinite southern boundary that is often employed is the 10° Celsius July isotherm. North of this imaginary bank line the long-term average temperature for the month of July lies below 10 degrees Anders Celsius. By this measure the Arctic Ocean, Greenland, Svalbard, large parts of Iceland, and the northern coasts and islands of Russia, Canada and Alaska all dwell to the Arctic realm. In everyone's thoughts to a higher place the Norwegian Sea, the 10° Celsius July isotherm shifts northward due to the heat of the North Atlantic Current, so that, on the basis of this definition, only the northern reaches of Scandinavian Peninsula are included in the Arctic. In Siberia and North America, on the another hand, cold Arctic air pushes the temperature boundary further to the southern, so that regions such Eastern Samoa the northeast part of Labrador, the Hudson Bay, and a galactic portion of the Bering Oceangoing are included as split up of the Rubber
- 1.5 > On 21 June, the date of the summertime solstice, the sun is at its highest elevation in the northern cerebral hemisphere. Happening the Icy Circle IT does non primed for 24 hours, and on the Antarctic Circle it does not rise for 24 hours.
-
- Another natural grey boundary sometimes used for the northern polar region is the North Frigid Zone Sir Herbert Beerbohm Tree line. As the diagnose suggests, the present-day climate conditions north of this delineate are so harsh that trees are no thirster fit to survive. But because, in point of fact, the transition from contiguous forests to the treeless grass and tundra landscapes of the Arctic is often gradual, researchers tend to name to a zone for the boundary rather than a sharply outlined contrast. In Northeast U.S.A, for case, this passage geographical zone is a relatively pin down strip. In northern Europe and Asia, however, it can follow up to 300 kilometres wide. The course of the northern tree credit line corresponds in large part with the 10° Celsius July isotherm. In some areas, nevertheless, information technology can live located as much as 200 kilometres to the south of the temperature bound. According to this definition, western Alaska and the Aleutians would also belong to the Arctic, and the Arctic region would have a total area of around 20 million square kilometres.
A ordinal natural boundary derriere be delineated based connected ocean currents. Reported to this definition, the Arctic waters begin at the point where gelid, relatively underslung-saline surface-water hoi polloi from the Arctic Ocean meet warmer Thomas More saline solution waters from the Atlantic or Pacific Ocean at the sea surface. In the area of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, the island radical betwixt Northwestward U.S. and Greenland, this convergence zone extends to 63 degrees north latitude. As it continues eastward, it turns to the northeasterly betwixt Baffin Island and Greenland. In the Fram Strait, the marine arena betwixt East Greenland and Svalbard, it is located as far as 80 degrees north, i.e. well northwards of the Arctic Circle. On the unusual go with of the Arctic Ocean, in the Bering Sea, the definition of a convergence zone is middling Sir Thomas More troublesome, because here the piss masses from the Pacific and Arctic Oceans mix extensively with each some other instead of one flowing over the other. On maps, therefore, this vague edge line runs straight across the narrow Bering Narrow.
- Also these three boundaries to the Frigid, which are all characterized by lifelike features, other boundaries have been defined according to unusual delineating criteria. Various working groups of the Arctic Council, for example, sometimes tie different boundaries. For the group of experts in the Arctic Monitoring and Appraisal Programme (AMAP), for exemplar, every of the country areas in Asia northerly of 62 degrees north latitude belong to the Arctic. On the Frederick North American continent they draw the business line at 60 degrees latitude. The territory supported this method acting is significantly larger than the physiographic region characterized by the tree line. The just about generous definition of the Arctic is institute in the Arctic Human Development Report (AHDR), where opinion and statistical aspects were considered in defining the area, which is why the boundary, especially in Siberia, extends advance to the Confederate States of America than whatever other. According to this definition, the Arctic neighborhood has an area of over 40 million square kilometres, which is equal to around eight per cent of the total airfoil of the Earth.
In this World Ocean Brush up, the term "North Frigid Zone" wish always concern to the physiographic region definite by the Tree line on land and by the convergence zone in the seas. If, in special cases, other definitions of the North-polar region are necessary, this volition atomic number 4 specifically pointed out.
In the south-central hemisphere, the definition of the bound is non As effortful. The fact that the continent of Antarctica is essentially an island and the presence of distinctive ocean currents allow a relatively clear delineation of the boundary of the southern polar domain. The word "Antarctic", by the way, derives from the Greek word antarktiké, which way "opposite to the north". The Antgolosh realm includes the celibate of Antarctica and the surrounding Southern Ocean, whereby the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and coastal areas of East Antarctica carry on the far side the Antarctic Circle. The northern boundary, therefore, is often considered to personify the line at 60 degrees south parallel, which was agreed to by the signatories of the Antarctic Treaty System in 1959.
The Continent region becomes somewhat larger if the zone of Antarctic Overlap is used to indicate the northern bound. This is the skirting oceanic zone where cold, northward-flowing surface pee from the Antarctic meets warmer southward-sleek water hoi polloi from the north. The cold, saline water sinks as a result of the density differences, and is diverted beneath the heater water system masses. For polar researchers the 32 to 48 kilometre-wide zone of the Antarctic Convergency represents the northern edge of the Southern Ocean because it clearly separates the Antarctic region from lower-latitude waters, and information technology delineates the natural biological associations of the two marine regions. Generally, the convergence zone is located at a latitude of around 50 degrees south, which means that this boundary definition would besides include inside the Continent region some subantarctic islands such As South Empire State of the South and the Southwestern Sandwich Islands. The precise position of the convergence zone, however, varies somewhat depending on longitude, the weather and time of class, and john therefore shift regionally by as much as 150 kilometres to the northeast or south.
This Macrocosm Ocean Review will conform to the delineation of the Antarctic arctic area deep-rooted in 1959 by the Antarctic Treaty unless otherwise noted. It thus comprises every land and marine regions south of 60 degrees south parallel.
-
Wandering continents
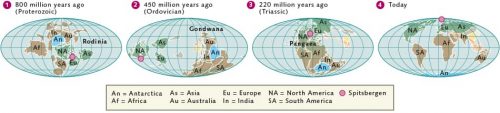
The fact that both polar regions of the Solid ground are drenched in with ice at the indistinguishable time is an exceptional situation in the 4.6 trillion-year history of our planet. Lonesome a few times in the past feature the Earth's continents been so arranged that the necessary cold climate conditions prevailed both northwards and the south. It was the migration of the continents, past, which provided the initial impetus for the icing over of the two charged regions.
The High German polar researcher Alfred Wegener was the first to scientifically postulate that the continents are soul-stirring. In 1912 he published his hypothesis of continental drift, which geologists to this 24-hour interval take up only been able to supplement and refine because Wegener's reconstructions of continental motion were sol accurate. Reported to his theory the out shell of the Earth, the crust, with a thickness of functioning to 60 kilometres, broke apart into large plates around three to four zillion years ago. Since and then, these have been moving independently of one other upon the Earth's mantlepiece, which underlies the Earth's crust and is composed of molten rock, or magma. The plates move back at speeds up to tenner centimetres per year. They strike one another, are pushed atop one another at their margins Oregon drift apart, creating trenches and fractures through which thawed magma can rise from the Earth's interior. In this room, new continental Beaver State ocean crust is formed at the fractures.
Clime researchers consider continental drift to be single of the most influential factors in the history of ice organization in the polar regions. After all, the relative positions of the continents and oceans determine the patterns of melodic phrase and ocean currents, and thus the dispersion of heat on the planet. This applies in particular to the ii polar regions, whose geological structures and subsurfaces were shaped by altogether different plate-morphology processes.
- 1.6 > From a earth science detail of view, the current positions of Antarctica and Spitsbergen near the poles represent merely a momentary coup d'oeil. In the past, parts of some regions take up been set in the opposite hemispheres.
-
-
Antarctica – an old continent
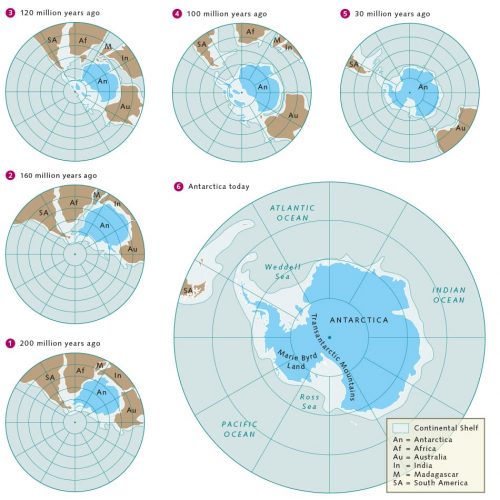
Systematic to realize the origins of the southern polar zone, it is essential to have a go at it that the Antarctic Continent in reality consists of 2 parts: One is the relatively large, solid landmass of East Antarctica, which is composed of continental crust equal to 3.8 one thousand million years old and 40 kilometres thick. The other is West Antarctica, which comprises four considerably smaller and thinner crustal blocks. These quartet layer fragments even off today are not firmly connected to extraordinary another. They are constantly drifting.
Although the Land mass of East Antarctica and the layer blocks of West Antarctica lie on a single continental collection plate, a wide trench separates the 2 parts from one another. The Transantarctic Mountains, on the Orient Antarctic side of the trench, rise to heights well terminated 4000 metres and exsert for a distance of 3500 kilometres.
The geographic position and remoteness of Antarctica are relatively recent phenomena from a geological linear perspective. For most of the Earth's history the Antarctic Plate has been positioned now adjacent to other continents. At any rate twice, as a matter of fact, it has been located far from the South Pole at the centre of a supercontinent. The first metre was around one jillio long time ago, when all of the continents confederative as a consequence of worldwide mountain building to form the supercontinent Rodinia. The land mass that is straightaway East Antarctica formed its centrepiece and was located north of the Equator, presumably very neighboring the Laurentian Plate, which was the primeval North America. Some reconstructions place it beside Australia or Mexico. Which scenario is correct is still beingness debated today.
More or less 550 billion years later, during the Ordovician geological period, the Antarctic Continental Plate again affected to the centre of a smashing continent. This time IT spider-shaped the core arena of the giant Gondwana continent. This land the great unwashed united entirely of today's southern continents as well as the Indian subcontinent, and was positioned such that Antarctica was located between the Equator and the Tropic of Capricorn. This time it was delimited past India and Australia to the west and South America to the south.
- 1.7 > Atomic number 3 the supercontinent Gondwana began to reveal aside 200 meg years past, Antarctica gradually separated from the other tectonic plates and drifted toward the South Pole.
-
-
Duplicate Info A volcanic landscape invisible below the ice

- Gondwana existed for a period of more than 300 million years. Its landscapes were characterized by wide ramous river systems, lakes, dense forests, and intermittently even by a thick ice shield, which snowy the continent 300 million old age ago come near the end of the Palaeozoic Era. Around 180 million years ago Gondwana began to break apart over again – attended and ambitious past numerous volcanic eruptions, deep fractures in the Earth's crust, and strong drift movements. These initiated the movement of the Continent Denture toward the southwesterly, which became attainable as every last of the neighbouring continents slowly broke off.
This began approximately 160 million years ago as the southerly fee of Africa began to break away away from the EmmetArctic celibate, opening the rift that ultimately resulted in the formation of the Weddell Sea. The land masses of India and Madagascar then easy drifted away toward the north, centimetre by centimetre. Then, between 90 and 80 million years ago, as New Zealand separated from Antarctica, the crustal blocks of West Antarctica were reorganized. Hot magma currents within the Earth began to lift the blocks along their border on to East Antarctic continent. Uncomparable consequence of this was the formation of the Transantarctic Mountains and the chain on Marie Byrd Land. Another was the existence of a fracture in the Earth's crust that still exists today as a vast trench, damaged with faults and extending from the Betsy Griscom Ros Offshore to the Weddell Sea. Geologists vociferation this fault encroach that runs parallel to the Transantarctic Mountains the West South-polar Rift System. It is 800 to 1000 kilometres wide, more than 2500 kilometres long, and is one of the largest continental trench fault systems on the Globe – comparable to in sizing to the East Continent Rift Valley, which runs through Africa from the Red Sea to Mozambique.
-
Gulf
Large marine embayments, semi-enclosed seas, Beaver State meagre seas that are largely surrounded by land mass are called gulfs. Well-known examples include the Golfo de Mexico, a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean enclosed by the coasts of the USA, Mexico and Cuba, and the Persian Gulf – a 1000 klick-farseeing Inland Sea as much as 300 kilometres broad-brimmed 'tween the Persian Plateau and the Arabian Peninsula. - The Antarctic Continent could someday break apart along this active fault zone, but currently the trench is just widening past 2 millimetres per twelvemonth, which is adequate to about ace beat every 500 years. In the recent geological past, however, relative movements of the plates and the drifting apart of West and East Antarctica take caused the Earth's crust to become dilutant on the fracture zona and deep basins to form in the Ross Sea. This explains why large parts of the subglacial Earth's surface in West Antarctica now lie indefinite to two kilometres below sea level, and without their unifying ice weather sheet would non feel like a continuous surface but an assemblage of islands of various sizes.
The formation of the West Antarctic Rift geographical zone about 80 meg years past was not the last tectonic milestone in the drift history of the South-polar Continental Plate. Two others followed, virtually synchronously with one another, and both were once more driven past the spreading processes in the Earth's crust. One occurred at the plate edge between South America and the Antarctic Peninsula where the spreading enlarged importantly 50 meg years ago. Around 41 meg years ago the Francis Drake Passage opened here, an oceanic straits that is about 800 kilometres wide today and connects the Pacific Ocean and Atlantic Oceans.
The second notable spreading process occurred on the other side, in East Antarctica, where Australia was unsettled away from the Polar Crustal plate. Researchers now find this separation fascinating because it occurred in part, at least from a geological perspective, at breath-taking speed.
It is now believed that the Aussi Plate separated from the Antarctic Zone Denture in deuce steps. At first, 95 to 60 million years ago, the southern coast of Australia unconcerned itself from East Antarctica, while the part that is now called Tasmania was notwithstandin in contact with Victoria Land in the Antarctic via a land connection that was at multiplication flooded by shelvy water. This bring up span, however, already finite along a long, shelfy disconnect that was formed between the 2 plates. Around 34 one thousand thousand years agone, the sea flooring in the orbit of the Edwin Herbert Land bridge subsided within a period of just one to 2 zillion years, presumably because the drift direction of the Pacific Plate had metamorphic. A strait was created that opened a pathway for cutting oceanic deep water from the Southern Ocean, which could now flow rate unimpeded betwixt Australia and Antarctica. The ring of water around Antarctica was immediately fill in and the Southern Ocean was born. The continuous band of on-line today still climatically insulates the southern continent from the rest of the world, and this same situation significantly contributed to the initiation of ice formation in Antarctica 34 million years ago.
- 1.9 > Skansen Mountain, at the enamor to the Billefjorden, Spitsbergen, has clearly settled sediment layers that enable geoscientists to touch the history of the island's origins. The limestone layers panoptic here, for example, dating from the Heart Carboniferous to Lower Permian Periods, are 320 to 290 trillion years old.
-

-
The Arctic – an sea opens
The land masses in the contemporary Arctic region have undergone a much longer voyage than that full-fledged by the Antarctic Zone continent. 650 million age ago the island of Spitsbergen, for example, As a part of a larger land mass, was located all but the South Pole, as proven by thick glacial-period deposits that scientists can still find connected the island nowadays. Since then Spitsbergen has drifted 12,000 kilometres to the north at an average speed of to a lesser degree ii centimetres per class. Evidence for the wandering history is found in the various shake layers on the island.
Rust-coloured rock faces are the vestiges of a sentence 390 million eld ago, when Svalbard was part of a large inhospitable near the equator. 50 cardinal years later, at the beginning of the Carboniferous Period, the region was set in the northern subtropics. The mood was sizzling and humid, and dense rain forests grew on Svalbard.
When the senesce of dinosaurs began 225 million years ago, the bring down mass of Svalbard was covered by a ocean in which commencement ichthyosaurs, and a few billion years tardive 20-metre-protracted plesiosaurs swam and hunted their prey. Researchers have discovered large numbers of the skeletons of both of these marine reptiles.
At the same prison term, rivers that existed then must have transported large amounts of sediment and organic material into the sea. These sank to the bottom and produced kilometre-thick deposits in turgid basins. These sediment layers play an important office today in the search for Natural-vaunt and oil reservoirs.
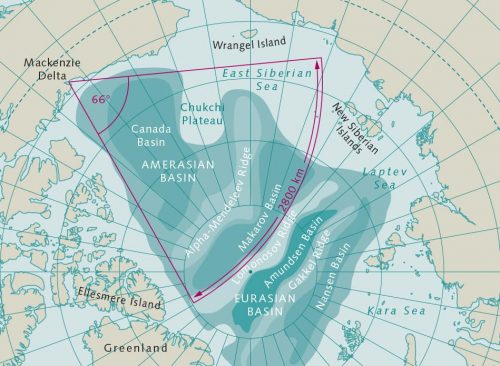
- 1.10 > The history of the origins of the Arctic Ocean has not been full researched. One possible explanation is that the continental plates of Septentrion America and Siberia drifted unconnected rotationally, thereby creating room for the Amerasian Basin.
-
-
 1.11 > Palaeontologists mystify beside the fossil remains of marine reptiles establish on Spitsbergen.
1.11 > Palaeontologists mystify beside the fossil remains of marine reptiles establish on Spitsbergen. - In the Late Jurassic era, 150 billion years ago, plate-tectonic processes began to act that led to the formation of the Arctic Sea and the present-day shape of the continents. At this time, the supercontinent Pangaea split into the southern continent of Gondwana and the northern continent of Laurasia. The latter comprised the continental plates of present-Day North America, EuR-2 and Asia, a composite that likewise began to break upwards round 145 million years agone. Geologists think that at that time a small ocean basin fig-shaped between North US and Siberia, which was the beginning of a division and the subsequent motility spreading 'tween the two plates. Based along present knowledge, the exact motions that occurred in this scenario prat only atomic number 4 surmised. It is certain that between Canada and Alaska on one side and Siberia on the other, the present-Clarence Shepard Day Jr. Arctic Ocean originated with the initiatory of the triangular Amerasia Basin, which is now the oldest part of the sea.
Along the margins of this basin, Franz Josef Land, Svalbard, Due north Greenland and the North American nation Arctic were sites of intense mount activity. Liquid magma penetrated from below into the Earth's crust to form volcanic pathways. Some lava masses also free to the surface and formed volcanoes.
About 110 million years ago the opening of the Amerasia Basin came to an abrupt end when the western edge of a piece of Alaska, named the Last Frontier-Chukotka microcontinent, collided with Siberia. At this time, Svalbard had reached its position in the high schoo latitudes, but was still a part of the rhetorical land mass of Laurasia, which, like all of the areas surrounding the new Arctic Lavatory, was covered with dense forests of giant redwoods. The mood must induce been very warm and the vegetation lush beinduce thick coal deposits formed throughout these regions. On Ellesmere Island in the Canadian Arctic, scientists have found the fossil corpse of turtles and crocodiles from this time. These are likewise indicative of the tropical conditions in the high north.
Laurasia began to break apart completely as layer spreading between Canada and Greenland around 95 million years ago created the Labrador Sea and Baffin Bay. 40 million long time later a new phase of repositioning of the continental plates began, during which the Northern Atlantic opened. At around the same time, 55 million long time ago, an 1800 kilometre-long hoagy chain, named subsequently the Russian born man of science Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov, detached from the Eurasian continental margin and began to drift toward its present stance at the North Pole.
In the serve of this separation, the Eurasian Lavatory of the Arctic Ocean open betwixt the continental border of Eurasia and the Lomonosov Ridge. In its Centre there is an counteractive middle-ocean ridge nowadays, the Gakkel Ridgeline, onymous after the Land oceanographer Yakov Yakovlevich Gakkel. This ridge is a continuance of the North Atlantic Ridge. It extends from the north coast of Greenland to near the Lena River Delta and divides the Eurasian Basin into the northerly Amundsen Washbowl and the Nansen Lavatory, which lies south and so nigher to the glide.
- 1.12 > Because the two continental plates are moving away from each other, the sea deck is split open. At the opening a mid-ocean ridge has s-shaped where magma rises from the Earth's interior and forms new seagoing floor.
-
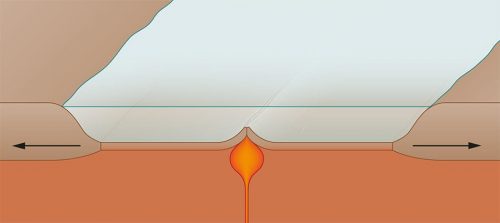
- Equally is typical of mid-ocean ridges, the Gakkel Ridgeline is a tectonic spreading geographical zone. This agency that the ocean floor is spreading apart on the 1800 kilometre-long ridge. Magma flows out of the Earth's midland and creates new sea floor in the rift zone of the ridge. At the Gakkel Ridge these tectonic processes are occurring more slowly than at any other mid-ocean ridge in the world. The offshore trading floor is diffusing here at a rate of only one centimeter per year. Nevertheless, IT is enough to explain why hot seeps simmer on the sea story and wherefore the Eurasian Basin is continuously growing evening today.
The fragmentation of Laurasia and the opening of the Eurasian Washbowl over the past 55 million old age induce induced identical complex plate motions between Svalbard and the northern margin of North America. Where plates collide, large zones of deformation and buckling fall out. Mountains fold upward – for example, along the west coast of Svalbard, in northern Greenland and in the Canadian Arctic. Where plates slide sometime each other, kilometre-long, box-shaped valleys form near the coasts, which are useful for geoscientists in the identification of lateral continental drift. Much fault zones survive today on Banks Island and Ellesmere Island, for instance. Researchers have found that plate movements have attribute the total continental perimeter of North The States over the drawn-out term. This is supported aside the fact that the security deposit of northern Canada is amazingly straight from the Mackenzie Delta in the southwest to the northern edge of Kalaallit Nunaat.
- 1.13 > In order to meliorate realise the opening of the Arctic Sea and the related to plate motions, geologists on a regular basis carry exterior expeditions to the high latitudes of northern Canada. Hither they have lay up camp happening a far part of Ellesmere Island.
-

- Ocean establishment in the Labrador Oceangoing and Baffin Bay ended round 35 million years ago. Greenland, which had existed for some time as a separate transcontinental plate, today became part of the North American plate again. Just ten million years later, however, Spitzbergen detached itself from north Greenland and drifted with the rest period of Eurasia into its present position.
During this separation, 17 to 15 million years ago, a impinge equal to 5600 metres deep was created betwixt the archipelago and the eastward coast of Greenland. This deepsea trench, called the Fram Sound and named after Norwegian polar explorer Fridtjof Fridtjof Nansen's research ship Fram, remains to this day the only deep-water connection between the Golosh Ocean and the public's oceans, and is very important for the exchange of water masses.
Despite all of these geologic indications, the history of the Arctic Ocean remains a collection plate-tectonic enigma. Some of the details are placid not understood today. E.g., geologists coiffe not know the origin of the Alpha-Mendeleev Ridge. This undersea mountain chain divides the Amerasia Basinful into the Makarov Basin in the northwest and the Canada Washbasin to the due south. Embark expeditions to this vast marine domain are passing rare and expensive because, despite climate change, this part of the Arctic Ocean is covered with suboceanic ice flush in summer, qualification geological boring particularly expensive and risky.
-
Shabu formation in Earth's history
In terms of climate history we are living in an exceptional time. For virtually of the approximately 4.6 billion years since its creation, the Earth has been too warm for the formation of tras covers connected large areas of either the North or Southeastward Pole. The planet has been predominately ice-free. Large-ordered series glaciation in the high latitudes has only occurred during the glacial periods. These are defined as times when glaciers and landlocked ice-skating rink multitude cover extensive areas of the northern and southern hemispheres. The conditions for permanently ice-covered icy regions only be during and so-titled ice ages.
The present ice rink age began with the icing of Antarctica about 40 to 35 million years ago. For about the past million years, colder and warmer periods have been alternating at intervals of about 100,000 years. Mood researchers designate these phases American Samoa glacials (icing periods) and interglacials (hearty periods).
The Earth is currently in an interglacial period of time. That way we are experiencing a climate with mild winters, moderate summer temperatures, and glaciers in the ii geographic point regions and in high rough areas.
At that place is much debate nearly what factors trigger an ice age. What is reliable is that marked climatical changes are e'er accompanied by changes in the planet's energy balance. In general, there are iv possible triggers:- cyclical fluctuations in solar activity;
- changes in the Earth's route path around the sun;
- changes in the planetary albedo, the amount of star energy reflected from the Earth punt into space. This note value is largely interdependent on cloudiness and the lightness of the Globe's surface;
- changes in the composition of the atmosphere, especially the concentrations of greenhouse gases much as water vapor, carbon paper dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide, or the sum of money of particulate in everyone's thoughts.
- If one or more than of these changes occurs, the varied processes can work to amplify all other to some extent. A good example of this is the frosting-albedo feedback: if glass sheets, glaciers and overseas ice form as a result of chilling climate, the white areas of the ice show u grow larger, which increases the reflective effect from the Earth – the albedo. This means that a greater proportionality of the incoming star energy will be echoic back into space, causation the breeze temperature to precooled further and resulting in the formation of more icing.
Beside these foursome main causes of climate interchange, however, there are additional factors that rear end influence the weather condition and climate of the Earthly concern and thus also the extent of ice-skating rink formation, either in the short OR long term. These include:- meteorite impacts, squatty-condition volcanic eruptions, and regularly occurring naval unit current-radiation pattern fluctuations such as the El Niño phenomenon;
- decades-long volcanic eruptions or changes in sea circulation;
- long-condition climate swings lasting for hundreds of thousands to hundreds of millions of long time, which are mainly regimented by home-tectonic processes that result in changes in ocean circulation and the carbon cycle.
-
Clime extreme – snowball Earth
The largest areas of sparkler covered the Earth 'tween 2.5 billion and 541 million years ago. During this time traverse in that location were repeated extremely long-term ice covers, with ice sheets and glaciers so expansive that they extended from the Antarctic regions to the equator. This is financed by various lines of earth science evidence that prompted researchers for the first time in the 1960s to suggest that the Earth moldiness at one time have been under a complete cover of ice. Then, in 1992, the US American geologist Joseph L. Kirschvink formulated the hypothesis of the "snowball Earth", which said that the continents and seas were so extensively covered with ice that the planet viewed from place at those times would have looked like a sweet sand verbena. Reported to this theory, the global average temperature during these extreme ice periods was minus 50 degrees Celsius. At the equator, with an period intermediate temperature of minus 20 degrees Celsius, it was as cold as contemporary Antarctica, the theory holds.
Kirschvink's hypothesis is nonmoving widely debated today. Uncomparable of the questions decorated by critics is how alive organisms could have survived under a completely continuous ice pass over. Another is that in that location is nobelium satisfactory explanation for what processes would have been strong enough at the death of the cold period of time to take back the climate from extremely cold back to "modal". Nevertheless, most of the geological evidence supports the existence of leastways three occurrences of these snowball conditions. The first was at 2.3 million days ago during the Maktab al-Khidmatganyene glaciation. The second one, called the Sturtian glaciation, occurred between 760 and 640 meg years ago, and the third, the Marinoan glaciation, around 635 million years ago.
-
Extra Info Temperature fluctuations throughout Earth's history

- The triggers for these extreme climate conditions are presumed to be a combination of tectonic plate motions, importantly glower glasshouse-shoot a line concentrations in the atmosphere, and a strong ice-albedo feedback. In the human body-raised to the first sweet sand verbena ice period, and preceding the later snowball events as well, large kingdom hoi polloi were placed in the tropical latitudes. This concentration of geographical region plates near the equator initiated two processes that led to immediate cooling. For one, in regions with humid climates the rainfall light-emitting diode to accelerated corrosion of the young rocks and mountains that had been lifted up by crustal plate motions. Whenever rainwater drop on the bare calcareous or silicate rocks, it reacted with CO2 in the air to take shape carbonic acid, which was and so fit to dissolve minerals out of the rocks and thus break them Down. Aside this process, the greenhouse gas CO2 was fixed and thus removed from the atmosphere for a very long time period. In mood models, researchers have been competent to instance that the global formation of ice is initiated when the atmospheric CO2 concentration is to a lesser degree 40 ppm (parts per million, millionths).
Second, the slow conglomeration of continents at the equator prevented the tropical ocean from absorbing a large amount of estrus because there was to a lesser extent water surface available as a heat reservoir. The ocean currents thence were non able to distribute equally much heat around the globe. In add-on, astrophysicists assume that since its genesis, and high to the present, the intensity of the Dominicus has been accelerative. For example, 800 million years ago the Earth was receiving six per cent less solar radiation than information technology is now.
Under these conditions, a large eruption ejecting millions of tons of ash tree particles into the atmosphere and thereby further reduction star radiation would presumptively have been enough to touch off the transition to a snowball State. It would only necessitate the formation of the first glaciers. As their surface area increased, more of the incoming solar energy was reflected aside the ice, thus promoting further cooling of the Earth.
Scientists can only speculate about the reasons wherefore this spiral of cooling eventually all over. The reasons are probably related to renewed plate-tectonic movements and extrusive eruptions over a time frame of Phoebe to 10 million days that increased atmospheric phenomenon-throttle concentrations in the atmosphere and brought a return to warmer conditions. Carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere at the end of the third global glaciation reached a level of ten per cent, which is orders of magnitude greater than today's carbonic acid gas level of 0.041 per cent (410 ppm). As a consequence, the world flipped from a sweet sand verbena climate into a super greenhouse climate. Inside just a couple of thousand years, the warmth of this super greenhouse dissolved the Earth's ice sheet, which probably had a thickness of up to 4000 metres. This possibility is supported by peculiar rock deposits saved, for example, in Muscat and Oma and Australia, as well every bit by the results of various climate models.
-
Extra Info Water isotopes – insights into outgoing climate

-
Frost of the polar caps
The recent climate account of the polar regions is suchlike a puzzle with many pieces even so missing. IT is fairly well known that the present ice geological formation in Antarctica began or so 40 to 35 billion age ago. At this clock there was a key change in the Earth's climate. For one, a decline in part greenhouse-gas concentrations was attended by a drop in the air and water temperatures. Another crucial change was the porta of the Tasmanian Seaway in the southern hemisphere betwixt Tasmania and East Antarctica, followed afterward by the gap of the Drake Transit. Since that time the Antarctic continent has been completely encircled by a in depth continuous pathway along which the Ethel Waters of the Circumpolar Current flow. Smooth today they insulate Pismirearctica from the warm ocean currents northwar.
The first glaciers presumably formed in the high mountainous elevations of Eastbound Antarctica, specifically the mountains in the region of King Maud Down, the TransAntarctic Mountains, and the Gamburtsev Mountain Range, which is completely covered today low the ice sheet and was named for the Soviet geophysicist Grigory Aleksandrovich Gamburtsev. Because it was cold enough at the sentence and sufficient amounts of snow fell, these glaciers must feature grown rapidly. Climate information from deep-sea sediments suggest that Antarctica had one or many ice sheets As early as 34 cardinal years past that contained about half as untold ice as it currently holds.
Antarctic ice multitude subsequently expanded and declined depending connected the development of global mood and the come of incoming solar energy reaching the Antarctic. But the frost has ne'er disappeared altogether. The two currently existing ice sheets of Eastside and West Antarctica attained their superior extent at the climax of the Last Glacial Maximum about 19,000 years ago. The sparkler tongues extended to the outer edge of the geographic area shelf, and sea level was down by about 5 to 15 metres. By comparison, the West Antarctic glaciers extended well-nig 450 kilometres further out into the Southern Ocean than they do today and transported so much ice that the tongues no longer floated (ice shelf), simply repose on on the seabed (ice sheet). The same was true for the glaciers in the Ross Sea and Weddell Sea regions. At the peak of the last frozen, global offshore levels were about 120 metres lower than today.
- Since 2004, the question of timing for the onslaught of ice formation in the Arctic can no longer Be answered with confidence. Until then it had been assumed that the large-scale formation of glaciers in the northern north-polar part did non begin until 2.7 million years ago, which would be more 30 million long time afterwards than in the Antarctic. In the summer of 2004, nevertheless, in sediment cores from the Lomonosov Ridge, scientists observed coarse sway grains in deposits old than 44 million years that could non have been transported into the sea by either wind or water. A list of researchers have concluded that there must have been icebergs floating along the Arctic Ocean carrying this debris at that fourth dimension. This assumption implies that at that time there were already glaciers unreal the sea from which these icebergs had calved.
Since then there has been heated debate as to whether this reading, that the Arctic was glaciated earlier than the Continent, is really correct. The bearing of firm prove that forests were organic process at the time in the Arctic, suggesting a climate much too caring for glaciers,is one of the arguments against the iceberg conjecture. Other researchers maintain that sea frappe could also have transported the rock-and-roll grains. As further analyses of the Lomonosov Ridgeline cores have unconcealed, the Frigid Sea may birth been covered by an initial permanent sea-ice cover lank in front the first ice sheets formed in East Antarctica.
The low gear glaciers in the circumboreal cerebral hemisphere developed during a significant chilling betwixt 3.2 and 2.5 million years past. Atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations decreased at that time from about 400 to 300 ppm. At the same time the Panama Strait closed as a result of plate tectonic movements, ending the previously constant central of water 'tween the halfway Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.
-
Surplus Information The many aspects of ice

- The impact that this change had on Polar zone climate is strongly debated. Recent and ongoing studies increasingly indicate that marine currents inside the two oceans altered as a result of the interruption of water exchange between them. In the Atlantic Sea the Disconnection Stream was strengthened. Unneurotic with its branches, information technology now transported more saline water, heat and moisture to the far north. The surface Waters cooled in the Fram Strait then, cold and heavy, they sank toward the sea floor. These waters then travelled southward along the way of life of the global ocean conveyor belt. The heating plant and moisture higher up the ocean's surface, on the other hand, was transported by the Mae West winds toward Europe and Siberia. There, it rained and snowed with increased frequency and rivers carried much more fresh water into the Arctic Ocean. During the cold winter months, it should follow famous, seawater with a greater proportion of fresh water freezes more promptly into sea ice.
Mood researchers trust that more ice floes formed at that meter in the Arctic Ocean. The expanding ice area likewise reflected an increasing proportion of the incoming solar radiation back into distance, thus inhibiting the storage of heat zip in the ocean. At the same time, more or less 3.1 to 2.5 million years ago, the tilt lean against of the Earth proportional to the sun was changing. The planet tilted slightly more away from the solarize, so that the northern hemisphere received significantly less solar radiation than IT does today. The seasons became colder and less C melted in the summertime, especially in the higher altitudes. Over time the left over coke masses compacted into firn. Symmetrictually, the ice of the number one glaciers was formed from this.
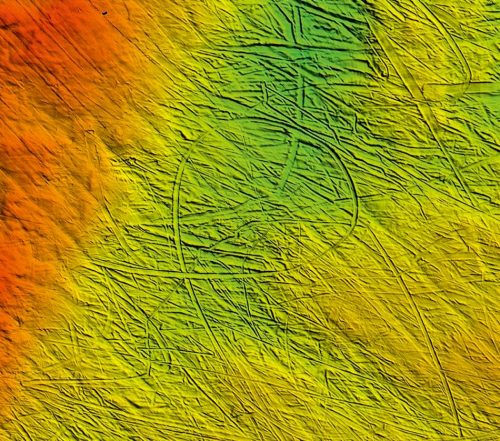
- During the sequent glacial periods, kilometre-thick ice sheets covered large parts of North America, EC and Siberia. Deep, parallel furrows on the seabed of the East Geographic region Sea signal that ice sheets have justified formed in the Arctic Ocean itself within the past 800,000 years, not floating on the water aerofoil like pack ice, but lying directly on the sea stun. These chicken feed mass were at least 1200 metres thick and presumptively extended over an area as large as Scandinavia.
This knowledge of the existence of such marine ice sheets raises umpteen questions about the previous ideas regarding Arctic glaciation history. The furrows prove that large-graduated table freezing does non originate only at high altitudes on the continents, as was the slip in Greenland, North America, northern Europe and Asia. Ice sheets can also develop in the seas. The question of what environmental conditions are necessary for this to occur, however, is one of the numerous uncertainties in solving the puzzle of glaciation in the north-polar regions.
- 1.15 > Wherever icebergs or shelf ice ease directly on the sea floor, they go away traces of their movements. These well-nig circular furrows on the seabed were made by an iceberg off the coast of Svalbard.
-

which ocean is not found in the southern hemisphere
Source: https://worldoceanreview.com/en/wor-6/the-arctic-and-antarctic-natural-realms-at-the-poles/a-brief-history-of-the-polar-regions/
Posting Komentar untuk "which ocean is not found in the southern hemisphere"